I have to admit, I love to deep fry foods. The high heat of deep frying can add flavor, making foods taste more decadent and savory.
It creates a delicious, crispy exterior while keeping the inside moist and tender.
The Maillard reaction, which occurs during frying, adds depth and complexity to the flavor profile.
The Maillard reaction is a complex chemical reaction that happens when proteins and sugars in food are heated together, resulting in the browning and flavor development of cooked foods.
Named after French chemist Louis-Camille Maillard, who first described it in 1912, this reaction is responsible for the rich colors and flavors in many fried, grilled, roasted, and baked foods.
The quality of the oil we use is crucial for the food’s taste and healthfulness. Rancid oil is one of the most significant hazards in deep frying.
In this blog post, we will examine rancid oil, its risks, and how to avoid it.
What is Rancid Oil?
When we talk about rancid oil, it means cooking oil that has gone bad due to oxidation, heat, or exposure to light.
When oil is exposed to air and high heat over time, it can develop off-flavors and unpleasant odors, telling us that it has gone bad.
Two types of rancidity can cause off flavors and odors in foods:
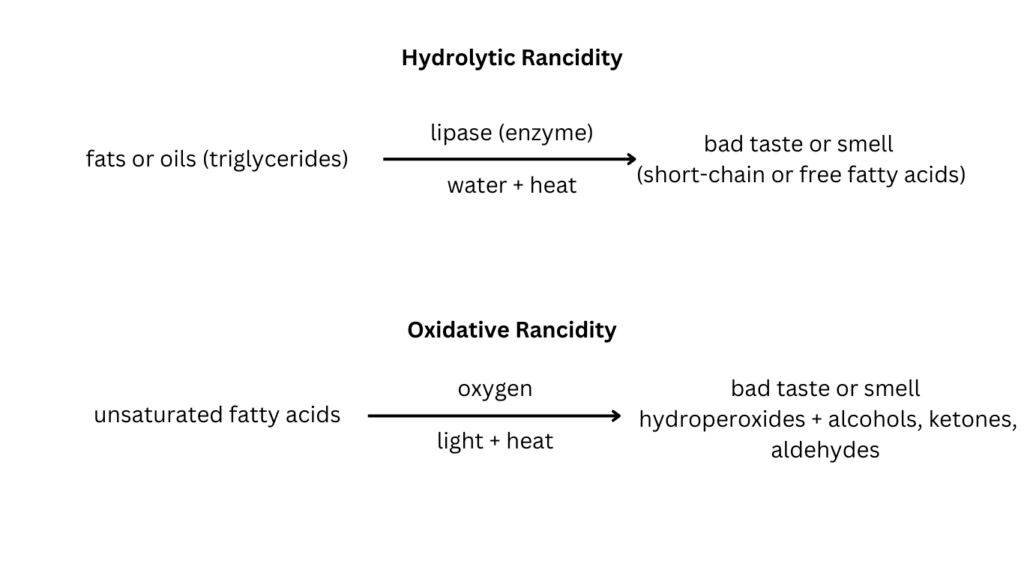
Both hydrolytic and oxidative rancidity can significantly affect the quality and safety of fats and oils.
Hydrolytic rancidity is more prevalent in dairy products (like butter) and oils stored improperly or contaminated with water.
Oxidative rancidity is common in oils high in unsaturated fats (like flaxseed or olive oil) and fried foods.
How To Spot Rancid Oil?
There are some obvious signs that we can look for when deciding to throw out the oil and use a new batch for frying:
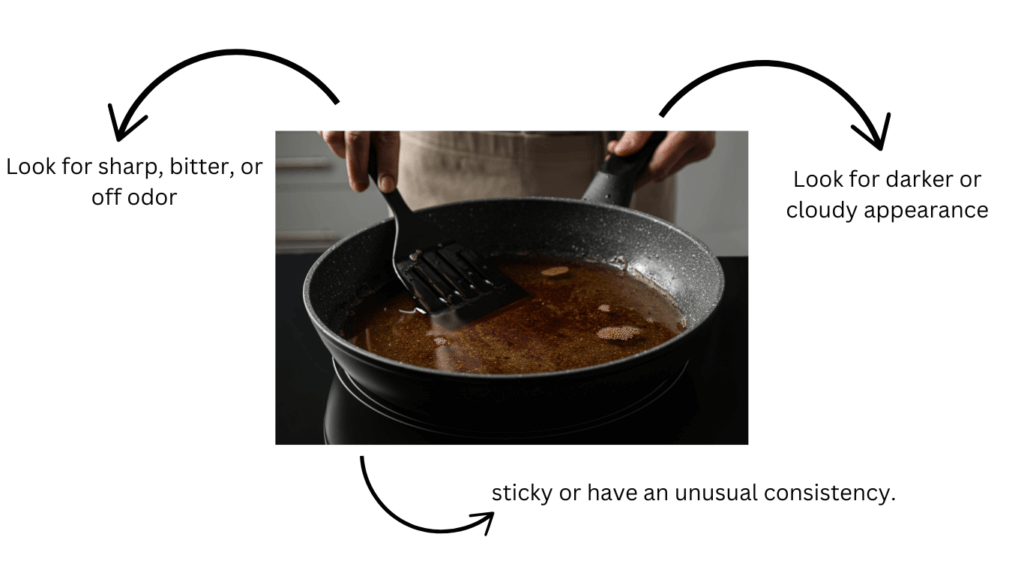
- Smell: Oil that has gone bad will have a sharp, bitter, or off odor.
- Taste: A small taste can help if you’re unsure. Rancid oil will have a stale or unpleasant flavor.
- Appearance: Fresh oil is always clear and sediment-free. Oil reused a lot may appear cloudy or have a darker color.
- Texture: While oil is usually smooth, rancid oil might feel sticky or have an unusual consistency.
- Foaming or Bubbling: If you notice excessive foaming or bubbling when you heat the oil, it may be a sign that it has gone bad.
Which Oils Are More Prone To Going Bad?
Any oil can become rancid, but certain oils, particularly those high in unsaturated fats, are more prone to rancidity due to their fatty acid composition.
Here are some oils that can go bad more easily:
- Flaxseed Oil, Walnut Oil & Hemp Oil
- These oils are high in omega-3 fatty acids, primarily alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), which are particularly sensitive to oxidation.
- Canola Oil
- Canola oil contains about 60% monounsaturated fatty acids, and the rest are Omega-3, Omega-6, and polyunsaturated fatty acids. While versatile in composition, it is still prone to oxidation.
- Corn Oil & Soybean Oil
- These contain a high level of polyunsaturated fats, which can become rancid more quickly.
- Sunflower Oil & Safflower Oil
- These oils are high in unsaturated fat content, making them susceptible to oxidation.
- Sesame Oil (Light)
- The refined version can be rancid-prone, especially if exposed to light and heat.
Hazards of Using Rancid Oil
- Perhaps the most obvious effect of cooking in rancid oil is that it will give a distinctive unpleasant smell and taste, which can ruin the flavor of fried foods. Instead of the delicious, crispy texture that we expect, foods may have an unpleasant aftertaste.
- Although frying in rancid oil will not immediately make you sick, it can contain harmful compounds like free radicals and aldehydes, which can lead to oxidative stress in the body. Regularly using bad oil may contribute to various long-term health issues, including inflammation and chronic diseases like heart disease and cancer. (Lobo, Patil, Phatak, & Chandra, 2010)
- Cooking in rancid oil can cause digestive discomfort, nausea, and diarrhea. The GI tract can become irritated and struggle to digest fats properly. (2011)
- Frying in rancid oil can result in uneven cooking and poor crispiness. The degraded oil doesn’t stick properly to food, affecting its texture and appearance, making it greasy and yucky!
How To Dispose of Rancid Oil Properly
There is a proper way to get rid of oil that has gone bad.
It is not advisable to just pour it down the drain. Rancid oil can clog pipes and cause plumbing issues, so we should avoid pouring it down the sink or toilet.
Always put the rancid oil into a container that can be sealed properly, like a glass jar or a plastic bottle. Make sure it’s tight to prevent leaks.
Check your local waste disposal guidelines. Many areas allow you to throw the sealed container in the regular trash.
Some recycling centers accept used cooking oil for conversion into biodiesel or other products like animal feed. Look for local programs or facilities that offer this service.




